Climate change is not just an abstract notion for many regions around the globe; it’s a pressing reality—and nowhere is this more evident than in Africa. A continent with diverse ecosystems and rich biodiversity, Africa is facing unique and formidable challenges brought about by climate change. However, the resilience of its people also shines through as communities and innovators rise to combat these changes. This article explores the climate change challenges Africa faces and the innovative solutions being developed on the continent to tackle them.
Understanding Africa’s Climate Change Challenges Ahead
-
Climate change isn’t just a future concern—Africa is experiencing its impacts right now. From erratic rainfall patterns to extreme temperatures, the continent’s agricultural sectors are particularly vulnerable. Many regions rely heavily on farming for their livelihoods, and changing weather patterns can have devastating effects.
-
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) suggests that rising temperatures could disproportionately affect Africa compared to other regions. With increased heat comes drought, which can lead to water shortages and hinder crop production. Many farmers are already struggling with unpredictable weather conditions.
-
Speaking of water, Africa is home to some of the world’s largest rivers, yet millions lack access to safe drinking water. Climate change exacerbates this issue, as prolonged droughts lead to diminished water sources. This widening gap between demand and supply can result in conflicts over water resources.
-
Coastal regions in Africa do not escape the impact of climate change either. Rising sea levels and stronger storm surges threaten coastal ecosystems, displacing communities and causing damage to infrastructure. Cities like Lagos and Mombasa are now facing the real risk of flooding, which can uproot lives and livelihoods alike.
-
Ecosystems are also under pressure. The African Great Green Wall initiative aims to combat desertification but still faces challenges such as land degradation and deforestation. The balance of these ecosystems is crucial for maintaining biodiversity and supporting local communities.
-
Climate-induced migration is becoming increasingly common as families are forced to leave their homes due to severe weather events. This movement can strain urban areas and lead to a host of socio-economic challenges, including job shortages and heightened competition for resources.
-
Health risks associated with climate change cannot be overlooked either. Higher temperatures can exacerbate the prevalence of diseases like malaria and cholera while diminishing food security—a combination that strains healthcare systems and populations.
-
Smallholder farmers are often hit hardest by climate change due to limited resources and access to technology. While they produce a significant portion of the continent’s food, the unpredictability of weather patterns can lead to reduced yields or total crop failure.
-
Many African countries rely heavily on fossil fuels for energy production, which presents a catch-22 situation. The ongoing reliance on these sources contributes to greenhouse gas emissions, while transitioning to renewable energy poses its own set of challenges, including infrastructure and cost implications.
-
Political instability in some regions adds another layer of complexity. When governance is weak, the ability to implement effective climate policies diminishes, making countries even more vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
-
Education and awareness are critical. Many communities are not fully aware of the implications of climate change or the necessity for action. Without proper understanding, it’s challenging to inspire grassroots movements or support for climate initiatives.
-
The intersection of poverty and climate change is also a critical factor. Many Africans live in impoverished conditions, making it difficult to invest in sustainable practices. Immediate survival often takes precedence over long-term environmental planning.
-
Climate finance remains a significant hurdle. While international aid exists, many African nations find it challenging to secure the necessary funds to implement wide-reaching climate strategies and resilience projects.
-
Wildlife conservation efforts are under threat as changing habitats create new challenges for Africa’s renowned biodiversity. Species face extinction due to habitat loss while poaching increases as communities look for alternative ways to make a living.
-
Ultimately, understanding the multifaceted challenges posed by climate change in Africa is critical for creating effective responses. It’s not just about mitigating climate impacts; it’s about fostering resilience and enabling local communities to thrive despite the odds.
Innovative Solutions: How Africa is Fighting Back Against Impact
-
Turning challenges into opportunities, many African nations are embracing innovative farming practices. From agroforestry to permaculture, farmers are integrating diverse plant species to build resilience against climate variability while boosting soil health.
-
Technology has become a game-changer. Mobile applications help farmers access real-time weather updates, which empowers them to make informed decisions about planting and harvesting. This tech-savvy approach improves yield and reduces waste, creating a more sustainable agricultural landscape.
-
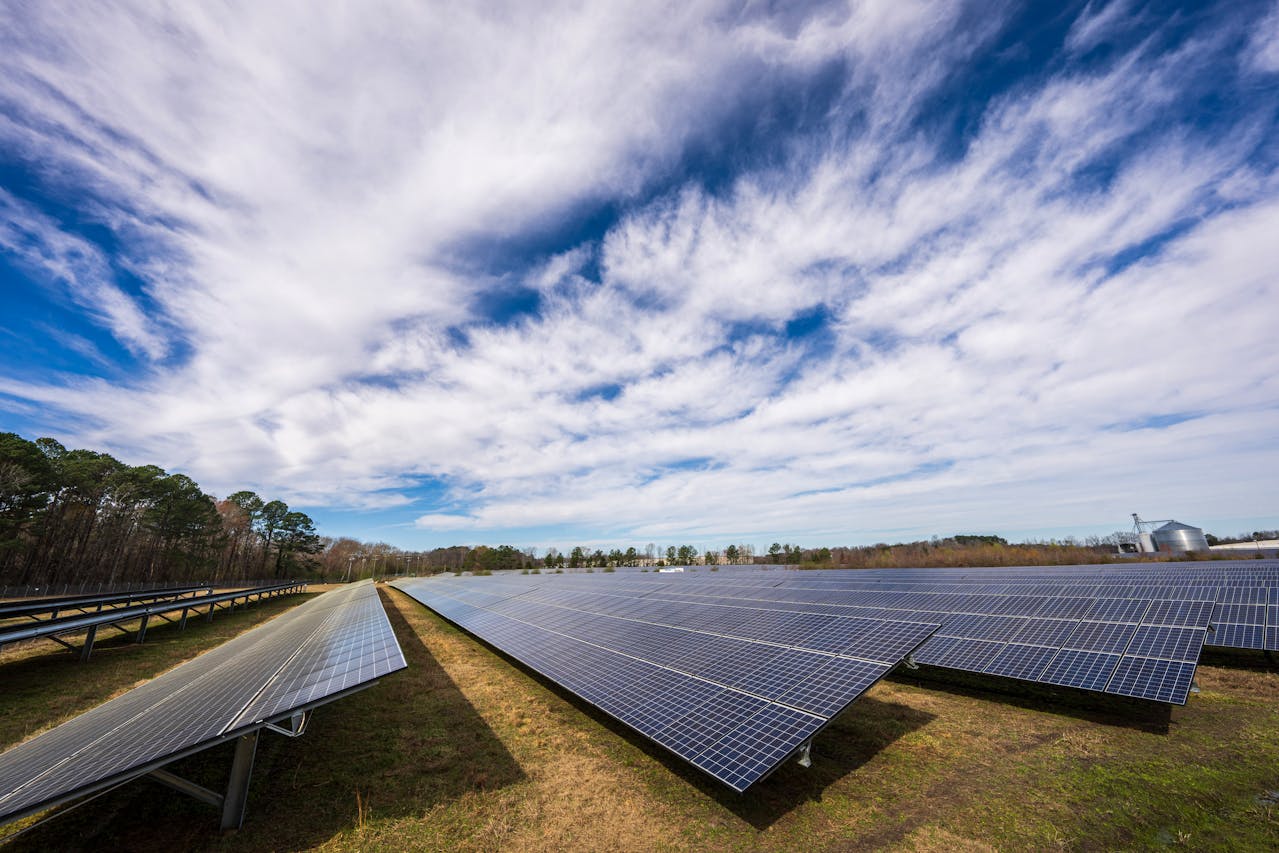
Solar energy is surging across the continent. Countries like Kenya and South Africa are investing in solar power as a clean, renewable energy source. Given the abundant sunshine, this presents an efficient and sustainable way to meet energy demands without further harming the environment.
-
Community-led conservation initiatives also play a pivotal role. Local groups are taking matters into their own hands by restoring degraded lands, protecting wildlife, and implementing sustainable land management practices. These initiatives not only benefit the environment but also strengthen community ties.
-
Innovations in water management are helping combat scarcity. Rainwater harvesting systems and small-scale irrigation projects enable communities to maximize water use during dry spells. By optimizing resources, these systems ensure that crops thrive even during unpredictable weather conditions.
-
Education and awareness programs are gaining traction in many African nations. Initiatives focusing on climate literacy aim to equip young people with the knowledge and tools they need to champion sustainable practices in their communities. This grassroots movement holds the key to a long-term cultural shift towards sustainability.
-
Another prominent initiative is the African Union’s Agenda 2063, which encourages all member states to develop climate-resilient economies. This framework underscores the desire for collective action to tackle climate-related challenges, promoting collaboration and shared responsibility.
-
Women are at the forefront of these efforts. Gender-inclusive practices ensure that women have access to resources, education, and decision-making in climate initiatives. Research shows that when women are empowered, communities thrive, generating a multiplier effect in combating climate change.
-
The growing trend of urban farming is also noteworthy. As cities expand, many urban dwellers are finding ways to produce their own food—ranging from rooftop gardens to community cooperatives. These urban farms not only provide fresh produce but also enhance community resilience.
-
Blockchain technology is being utilized to enhance transparency and traceability in agricultural supply chains. By ensuring that farmers get fair prices and consumers know where their food comes from, this technology builds trust and fosters sustainability.
-
International partnerships and donor-funded projects are helping to bolster innovation. Collaborations with NGOs and global organizations enable Africa to implement cutting-edge climate solutions while pooling resources and expertise.
-
Eco-tourism is also on the rise, encouraging conservation while providing an economic boost for local communities. By promoting sustainable travel, countries can generate income while protecting their priceless natural heritage from the impacts of climate change.
-
Circular economy initiatives are being adopted, encouraging waste reduction and promoting recycling. By finding ways to reuse materials, communities can lessen their environmental footprint and foster economic growth.
-
The youth climate movement is gaining momentum, with passionate young people advocating for policies aimed at sustainability. Their collective voice brings attention to climate justice and ensures that the younger generation is active and involved in shaping a sustainable future.
-
Finally, collaboration on a continental scale, exemplified by initiatives such as the African Adaptation Initiative, aims to pool resources and ideas to foster resilience. By leveraging shared knowledge, African nations can mitigate climate impacts and pave the way for sustainable development across the continent.
As we navigate the complexities of climate change in Africa, it becomes clear that while challenges abound, so do innovative solutions. The resilience, creativity, and determination of people across the continent are testament to a brighter future. By embracing sustainable practices, leveraging technology, and fostering community involvement, Africa is not just fighting back against climate change but reimagining its relationship with the environment. The journey ahead is indeed challenging, but Africa proves that with innovation and collaboration, hope is very much within reach.